Robotic surgery was initially developed by researchers at NASA Research Center with the aim of performing surgeries on astronauts in space. It was first attempted in 1997 with robotic cholecystectomy (gallbladder surgery) and approved for medical use by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2000. Experts from Özel Adana Ortadoğu Hospital explained key aspects of the Da Vinci Robotic Surgery System.
The Da Vinci Robotic Surgery System has been successfully applied in various medical fields for over 25 years, including general surgery, gynecology, urology, thoracic surgery, ENT, and pediatric surgery. Globally, it has been utilized in over 12 million surgeries, offering surgeons enhanced precision and control during operations.
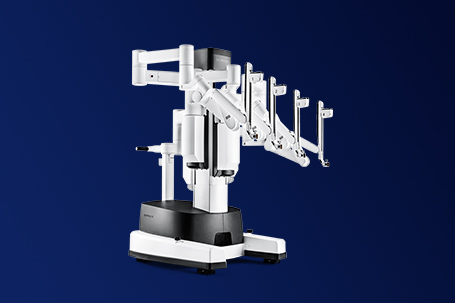
The Da Vinci Robotic Surgery System consists of three main components:
This is the main unit where surgical intervention is performed and where the robotic system connects physically with the patient. It includes four robotic arms: one equipped with a high-resolution 3D endoscope and three others controlling surgical instruments guided by the surgeon. These arms are designed to perform more precise and delicate movements than a human hand, effectively executing minimally invasive procedures in confined areas.
This is the central unit where the surgeon operates the robotic arms. The console allows the surgeon to view and manage the procedure using a high-definition 3D stereo imaging system. The ergonomic design enables the surgeon to work comfortably, with a touch panel for zoom, focus, and image adjustments. Foot pedals provide additional controls independent of hand movements, enhancing precision during the operation.
The vision tower handles the visual operations of the robotic system, processing and displaying endoscopic images in real-time. It also includes an energy unit and a touch screen interface for easy adjustment of imaging and energy settings. Fiber-optic cables connect this unit to other components, ensuring seamless data and power flow for uninterrupted control and visualization.
Robotic surgery is effectively used to treat a wide range of conditions across various medical fields:
Robotic surgery is commonly used in urology, particularly for prostate cancer. It minimizes complications such as erectile dysfunction and urinary incontinence by preserving nerves around the prostate. It is also employed in surgeries for kidneys, bladder, and testes.
The use of robotic surgery in gynecology has grown significantly. Procedures include hysterectomy, myomectomy, operations on fallopian tubes, and sacral hysteropexy for correcting vaginal prolapse.
Robotic surgery is widely utilized in general surgery for colon and rectal cancer, bowel diverticula, inflammatory bowel diseases, and rectal surgeries. It is also prominent in bariatric surgery for procedures like sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass.
This method is used for treating lung cancer and mediastinal tumors. Procedures such as removal of lung nodules, segmental resections, and lobectomy are performed with minimal incisions, resulting in faster recovery and reduced post-operative pain.
Robotic surgery is applied in coronary bypass, treatment of arrhythmias, and valve disorders, particularly in cases unresponsive to other treatments.
Transoral robotic surgery is employed for tumors and cysts in the larynx, pharynx, tonsils, tongue, and oral cavity without external incisions.
Robotic surgery is also used in pediatric cases requiring minimally invasive techniques, particularly in urological and general surgery. It reduces trauma and accelerates recovery in young patients.
Robotic techniques are used for weight-loss surgeries like sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass, enabling more precise procedures with lower complication risks.
Da Vinci robotic surgery offers several key advantages over traditional methods:
Smaller Incisions: Robotic surgery involves smaller incisions, resulting in faster recovery and lower infection risk compared to traditional methods.
3D Imaging: The system provides high-resolution 3D and magnified images, offering better visualization than traditional methods.
Precision and Control: Robotic arms provide greater dexterity and precision, enabling access to challenging areas and delicate interventions.
Less Pain and Faster Recovery: Smaller incisions result in less post-operative pain and faster healing.
Reduced Blood Loss: The precise approach minimizes blood loss during surgery.
Surgeon Comfort: Surgeons perform operations seated at a console, reducing fatigue compared to standing for extended periods in traditional surgeries.
Advanced Technology and Advantages of the Da Vinci Robotic Surgery System
Stapler Technology: Equipped with microsensors that measure tissue thickness over 1,000 times per second, providing safer cutting and sealing.
Energy Instruments: Articulated tools with advanced energy adjustments protect nerves, preserving sexual, urinary, and sensory functions.
3D Optics: The 3DHD visualization system offers enhanced depth perception and detailed anatomical views.
Firefly Fluorescence Imaging: Near-infrared technology visualizes blood flow and tissue perfusion, aiding decision-making during cancer surgeries and lymph node dissections.